This article explains how to launch the Registry Editor, create, and apply a REG file in the Windows 10 operating system.
How to Open the Registry Editor
Opening the Registry Editor is very simple — you can use any of the following methods.
Opening the Registry via the Run dialog
Press Win + R on your keyboard.
In the Run window that appears, type regedit and click OK.

If you are logged in with an administrator account and have User Account Control (UAC) disabled, the program will launch with administrator privileges.
You can also open the Registry Editor using other methods described in our article “How to Open the Registry Editor in Windows 10.”
Creating a REG File Using a Text Editor in Windows 10
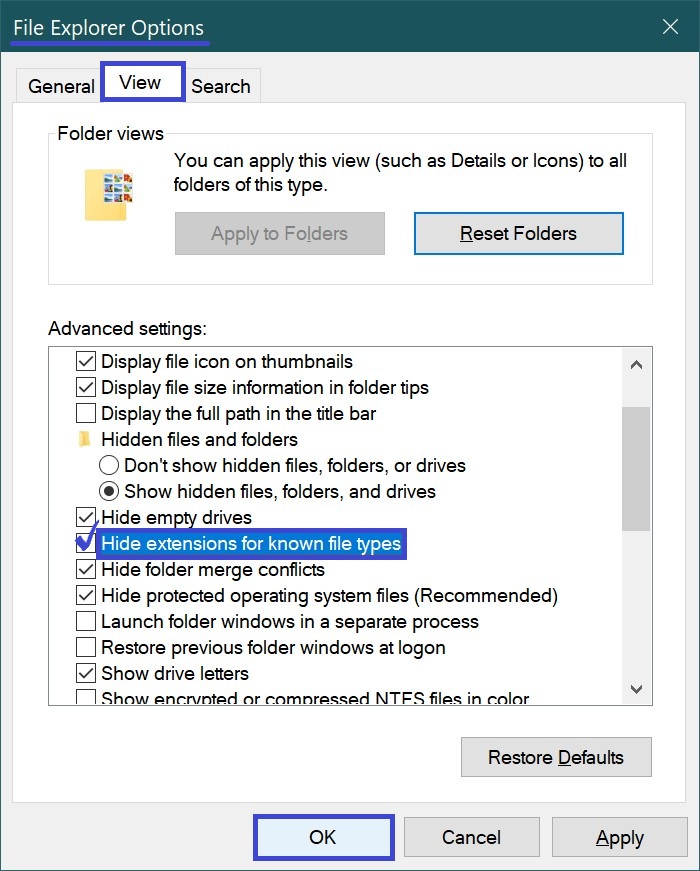
The first thing you need to do is enable the display of file extensions — by default, Windows does not show them.
To do this, open the Control Panel, set View by: to Small icons, and select File Explorer Options.

In the File Explorer Options window that opens, go to the View tab and uncheck the option “Hide extensions for known file types.” Then click OK.
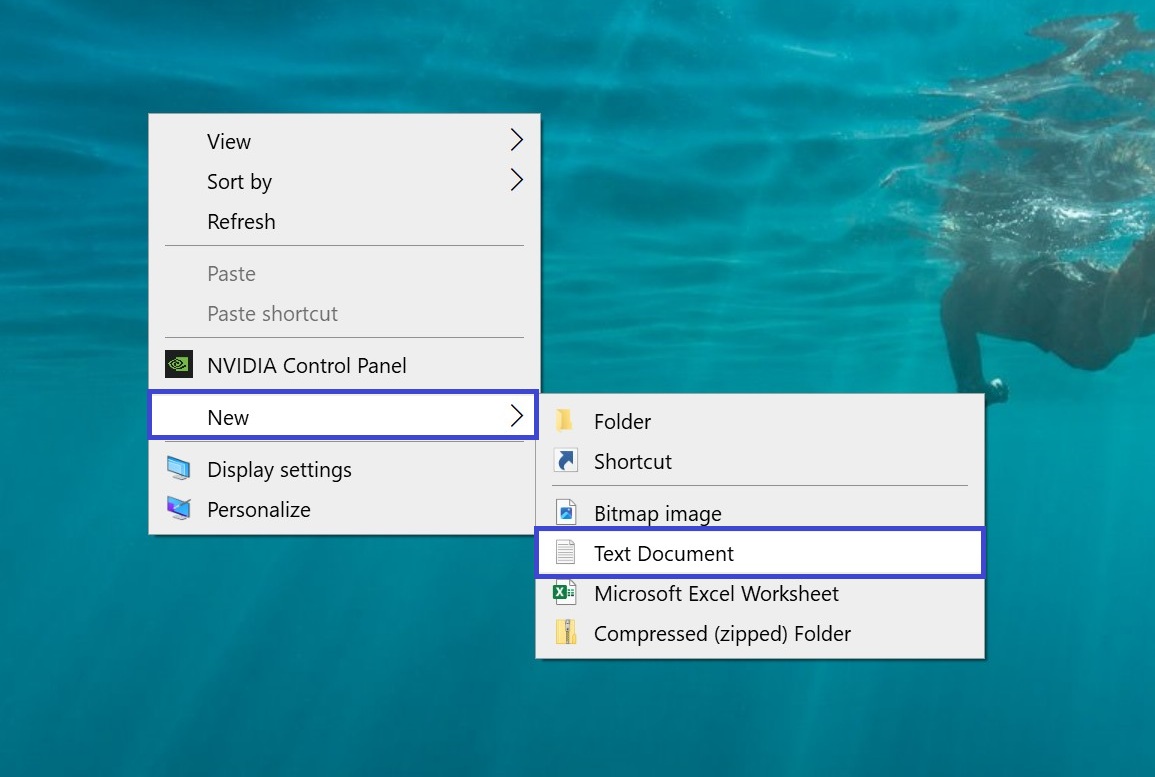
Now you can proceed to create the REG file. To do this, right-click on any empty area of the desktop, and from the context menu, select New → Text Document.
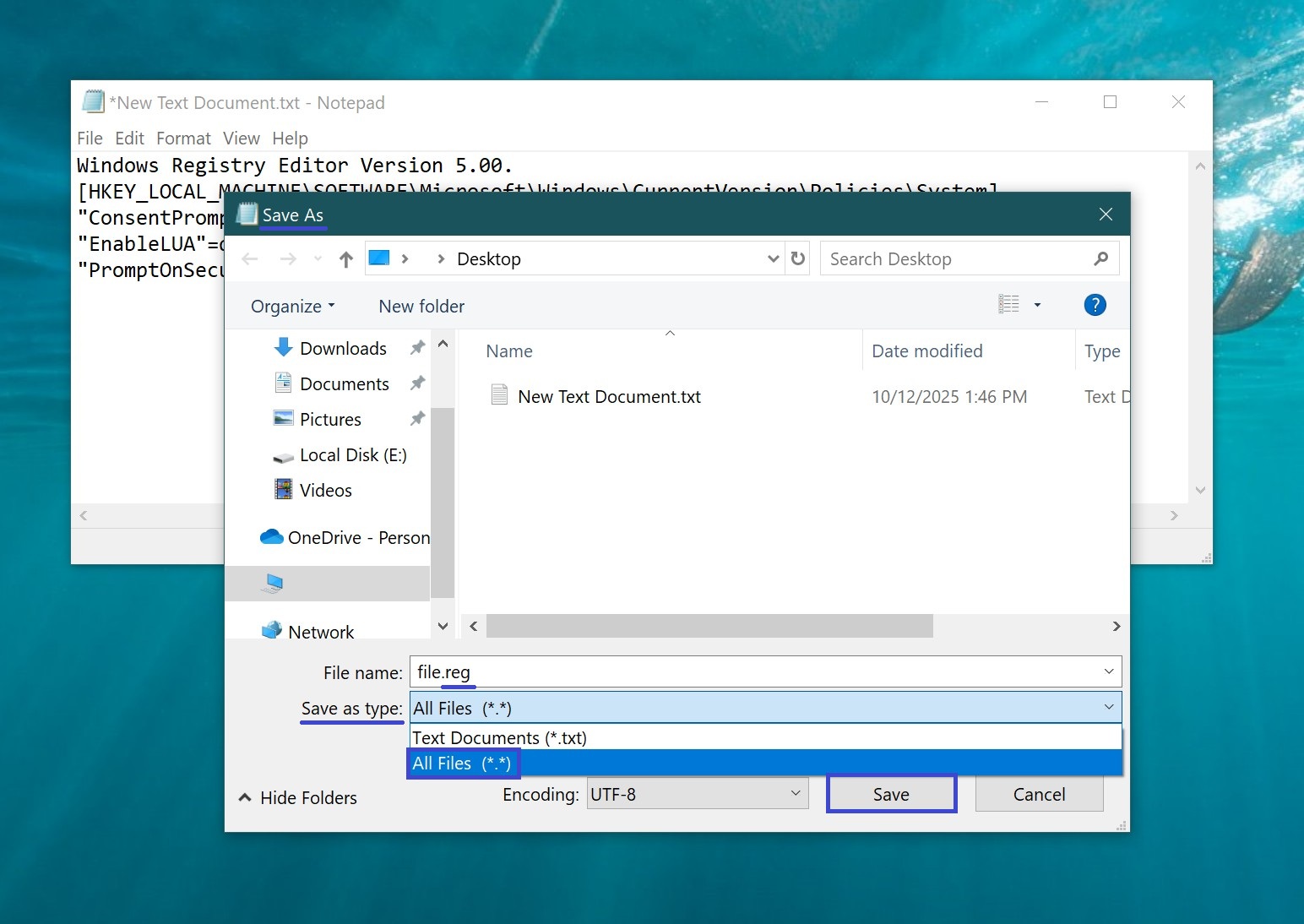
Open the newly created document (by default, it will open in Notepad), then copy and paste the required code into the program window.

In the File menu, select Save As… (CTRL+Shift+S). In the Save as type dropdown list, make sure to choose All Files, specify the save location, and include the .reg extension in the file name. Then click Save.
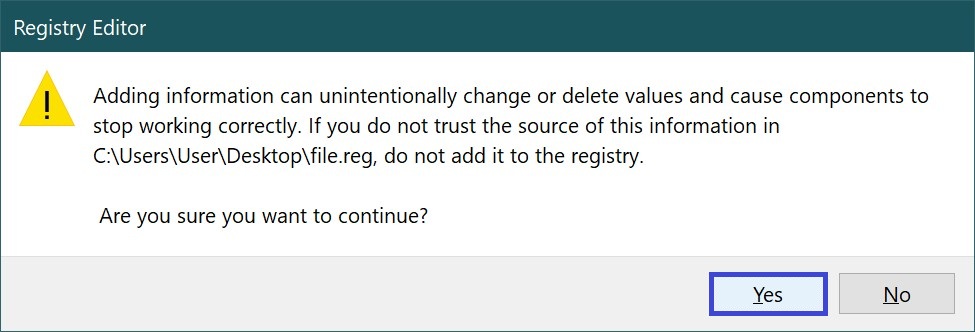
Once the file has been saved, you can add its contents to the registry. Double-click the file and confirm your intention to make changes to the registry by clicking Yes.
Applying a REG File
There are several ways to make changes to the registry.
Double-click the REG file with the left mouse button.

In the window that appears, click Yes to confirm.

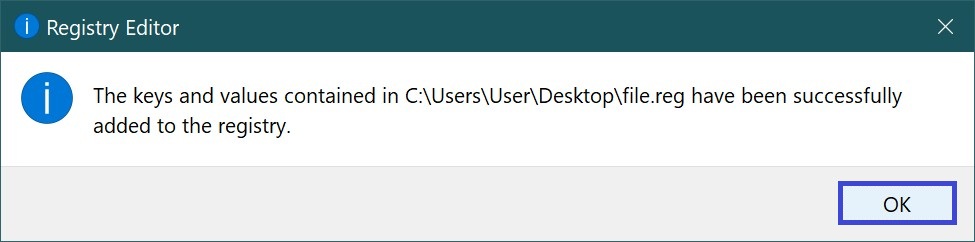
In the next window, click OK.
Another option is to right-click the REG file and select Merge from the context menu.
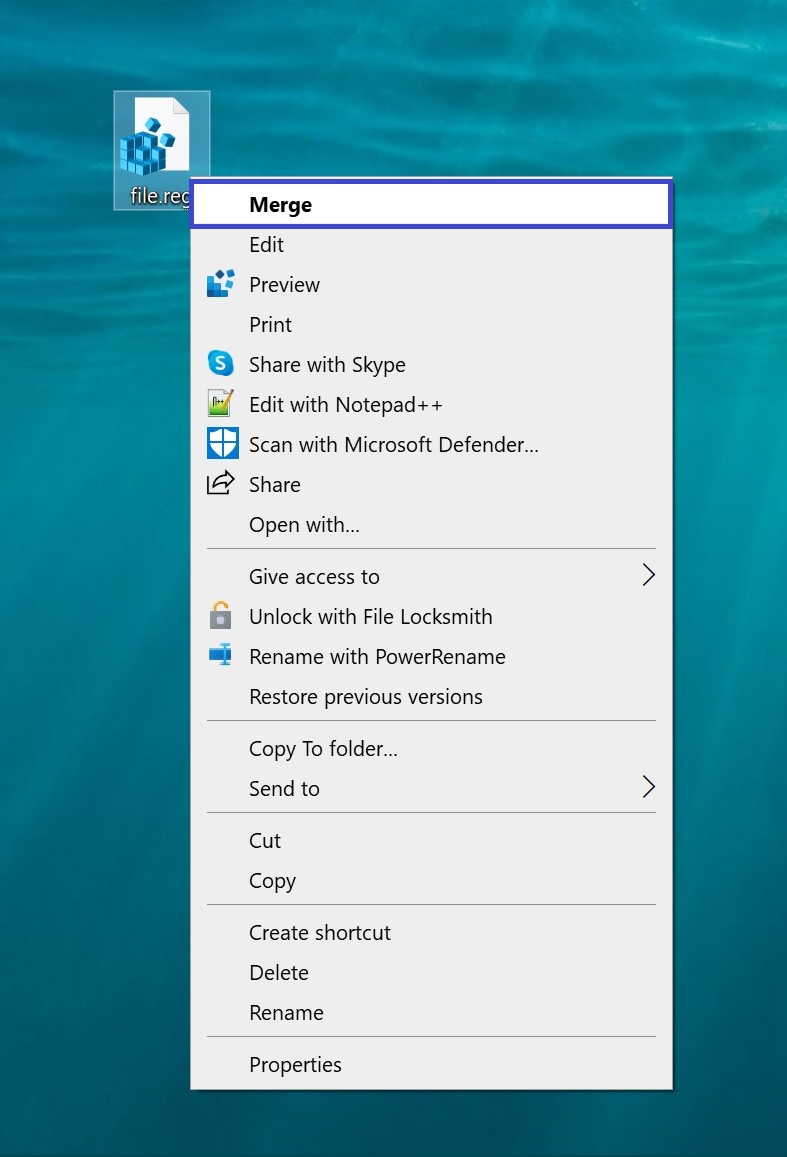
In the window that appears, click Yes.

In the next window, click OK.

In the third method, you’ll need to use a command.
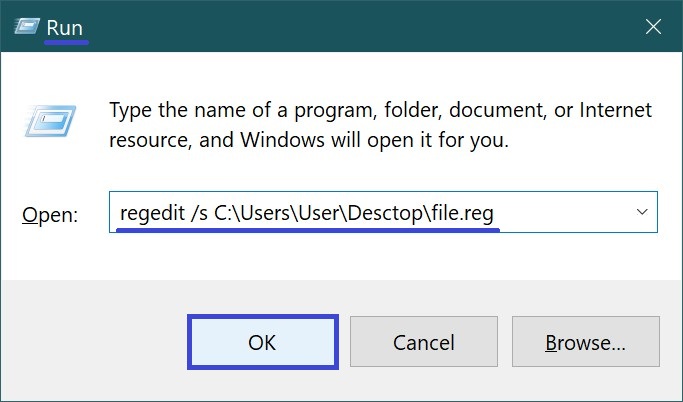
Press Win + R, and in the Run dialog box, type the following command:
regedit /s Path_to_file\File_name.reg
Then click OK.
For example:
regedit /s C:\Users\User\Desktop\file.reg
To apply many REG files, you need to be logged in under an administrator account, and User Account Control (UAC) must be disabled.
And for the fourth method: press Win + X and, in the context menu that appears, select Command Prompt (Administrator).

In the window that opens, type the following command:
regedit /s Path_to_file\\File_name.reg
Press Enter ↵.
For example:
regedit /s C:\Users\User\Desktop\file.reg

If the registry already contains a parameter that the REG file is trying to add, applying the REG file will replace the existing values with the new ones.