MSConfig (Microsoft System Configuration Utility) is a built-in Windows operating system utility which can be used to modify system startup options, change boot parameters, enable or disable services and programs that run on system startup, and run various diagnostic and statistical utilities.
Via the “Run” window
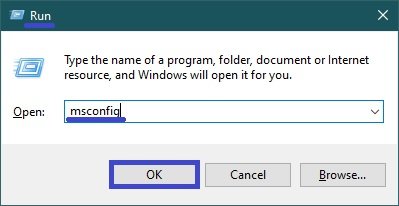
To open the msconfig utility this way, press Win + R, in the Run window that opens type (copy and paste) msconfig and press Enter↵.
Using “Search”
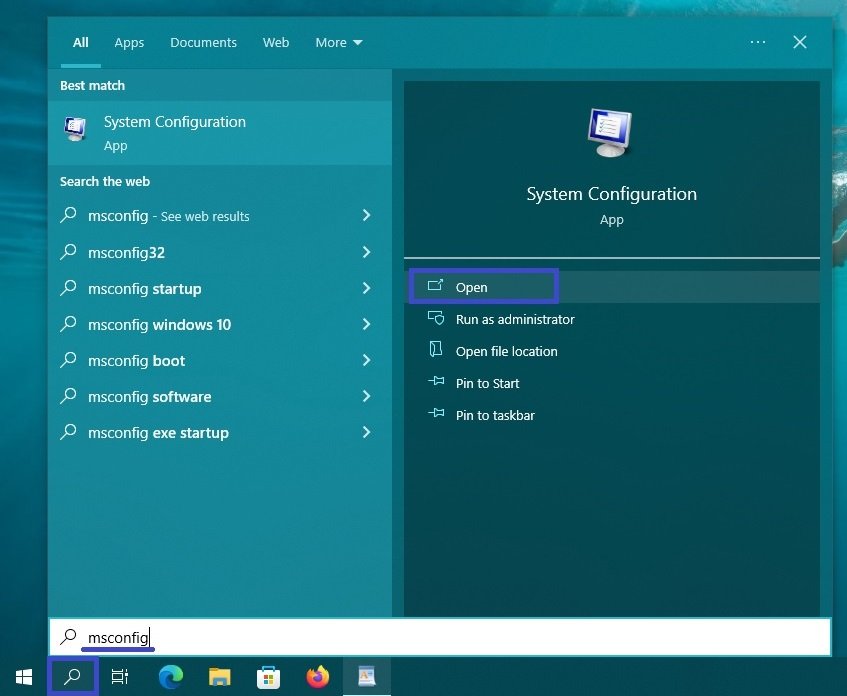
To open the msconfig utility use the “Search in Windows” by clicking on the search icon in the taskbar or pressing the Win + S key combination, in the search bar start typing msconfig and in the search results select System Configuration.
Via “Windows Administration Tools”
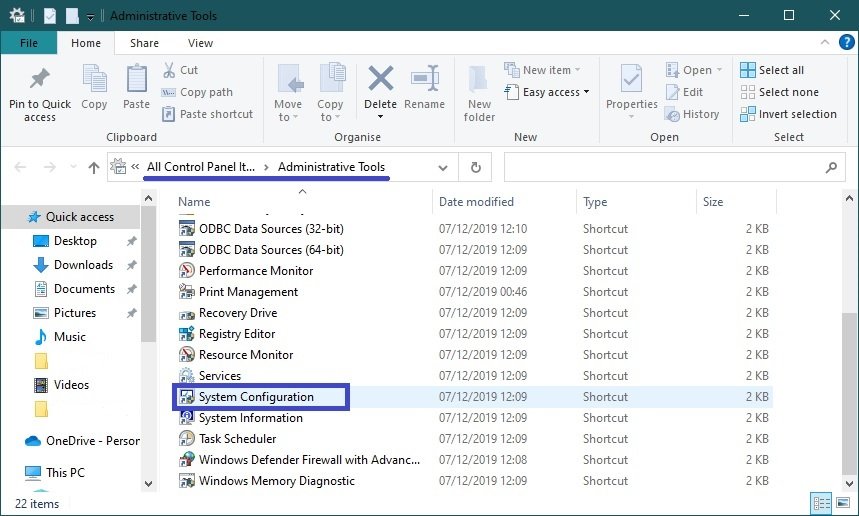
Open the “Windows Administration Tools” and select System Configuration in the “Administrative Tools” folder.
In the Windows 10 Start menu
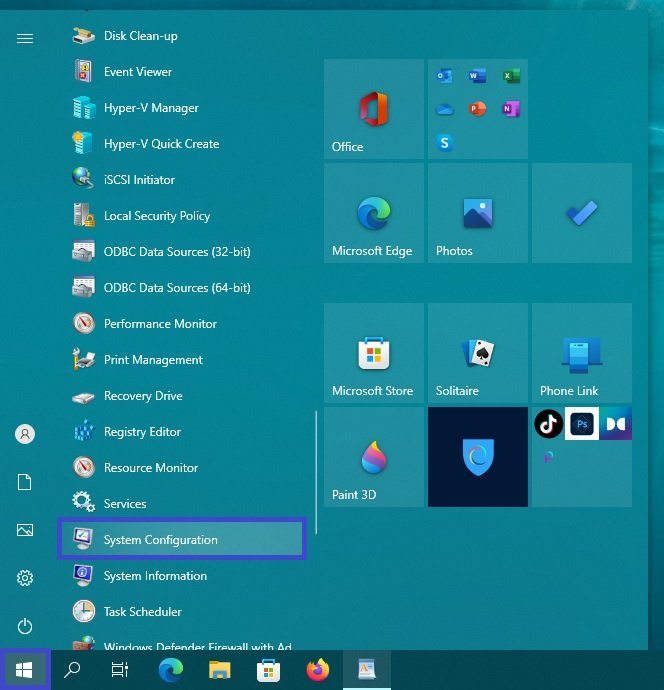
Open the Start menu, then in the list of applications in the group under “W”, locate and expand the “Windows Administrative Tools” folder and select System Configuration.
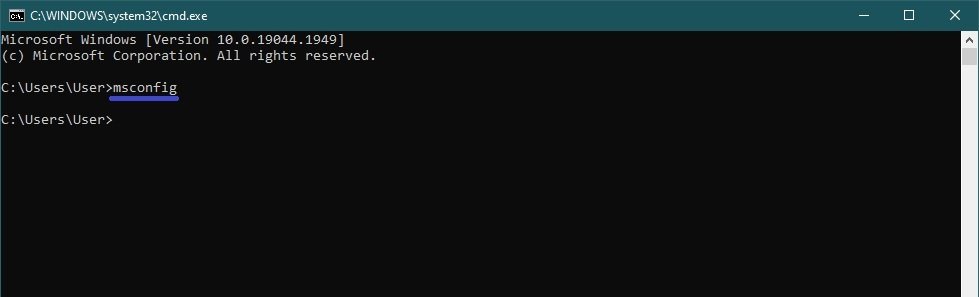
Using the command prompt
To open the msconfig utility at the command prompt, run the command line and execute the command:
msconfig
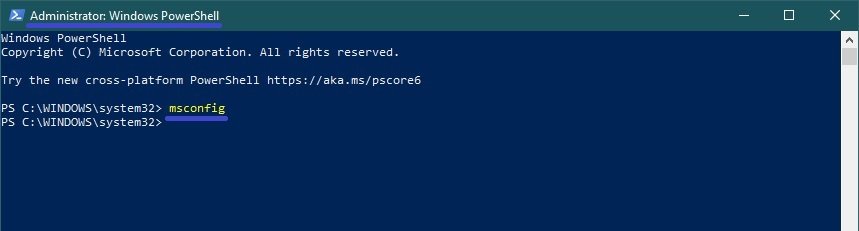
In Windows PowerShell
You can also open the msconfig utility in the PowerShell console by opening Windows PowerShell and running the following command:
msconfig
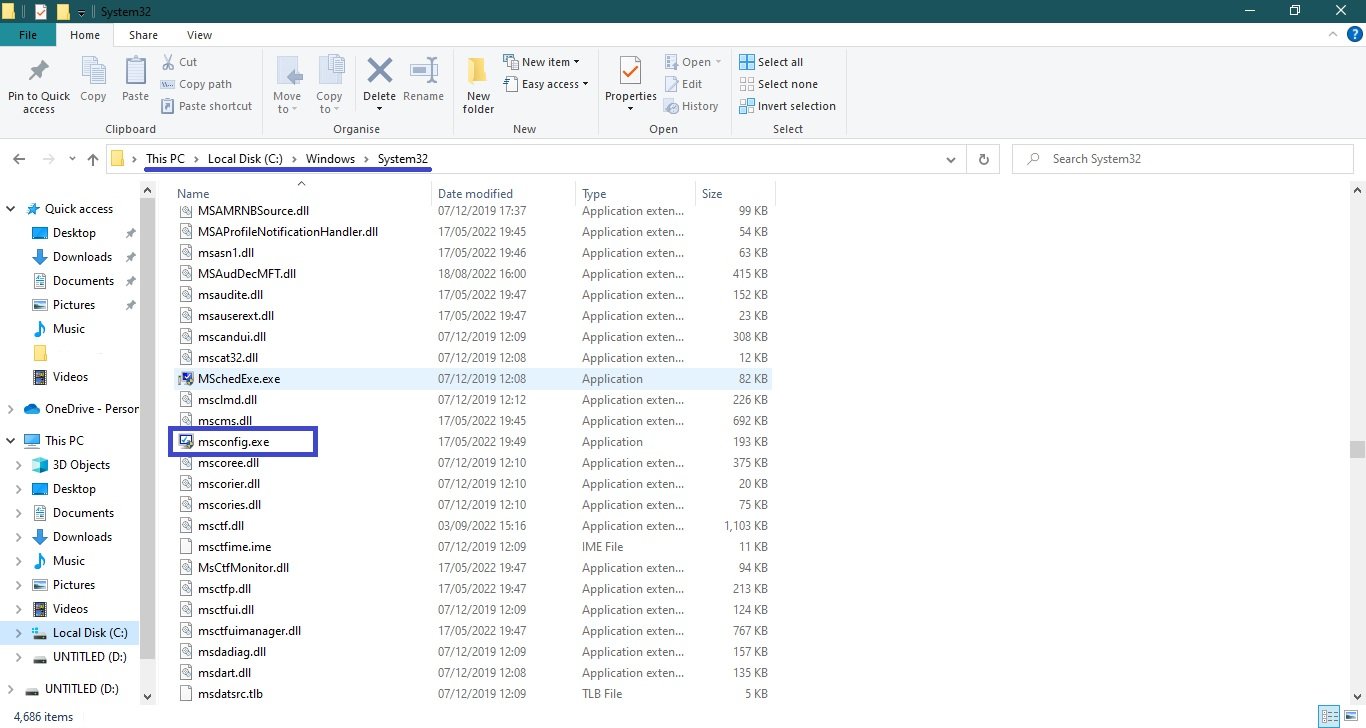
In the “System32” system directory
Open Windows Explorer and navigate to the following path:
C:\Windows\System32
Then, to run the msconfig utility, locate and double-click the msconfig.exe file
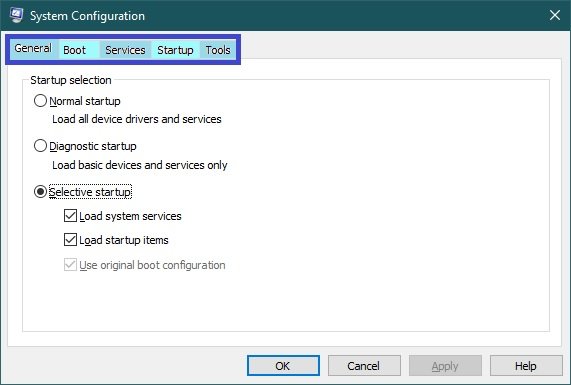
General information about msconfig
The msconfig (system configuration) utility is a five-tabbed window:
- General
- Boot
- Services
- Startup
- Tools
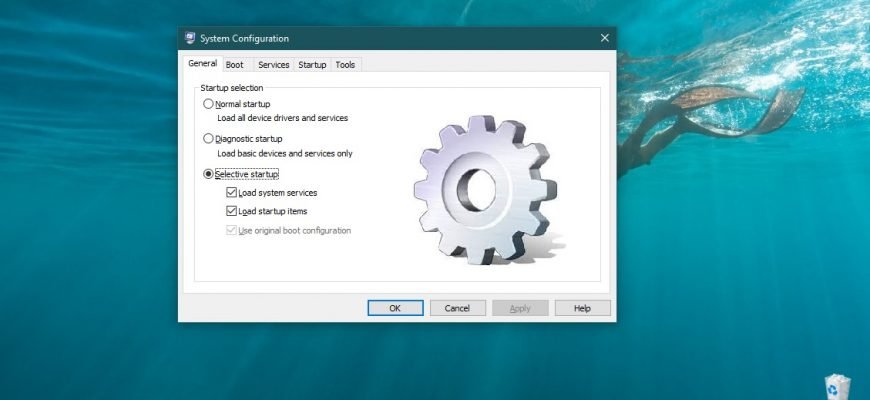
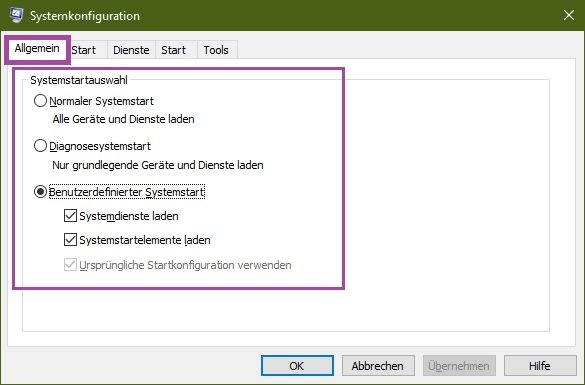
General
The General tab allows you to select the download option: Normal, Diagnostic or Selective. Diagnostic startup loads only the main drivers and starts the main services. Selective start allows you to choose whether to load system services (usually required) and autorun items (can be disabled if the cause of the failure is an automatically started program).
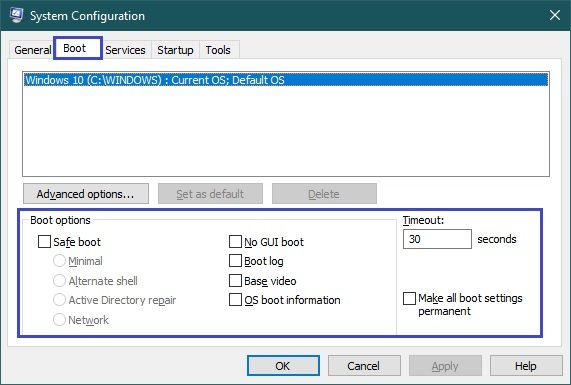
Boot
The Boot tab allows you to set additional options for booting your operating system, for example you can enable the system to boot into safe mode to diagnose various problems.
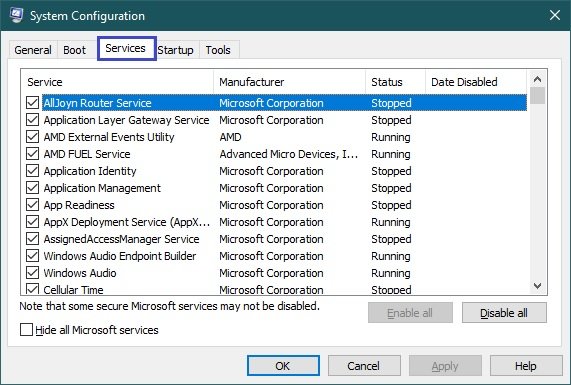
Services
The Services tab allows you to enable or disable services for diagnostic purposes. For example, if an error occurs, you can disable services one by one until the error disappears. This will help you find out which service is causing the problem. You can also enable the “Don’t show Microsoft services” filter here, which allows you to hide Microsoft services, so that only third-party services remain visible.
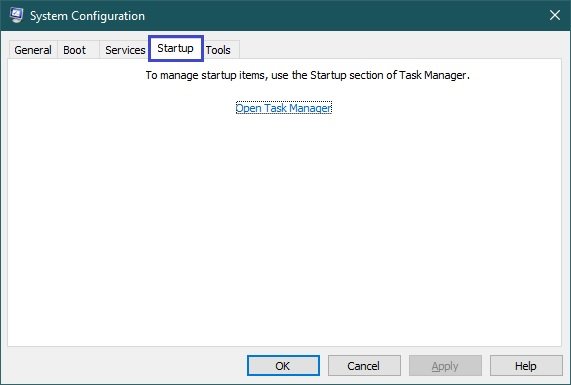
Startup
The Startup tab allows you to enable or disable various applications and services that use autoloading on system startup.
On Windows 8, Windows 8.1 and Windows 10, you should now use the task manager’s “Startup” section to manage the autorun items.
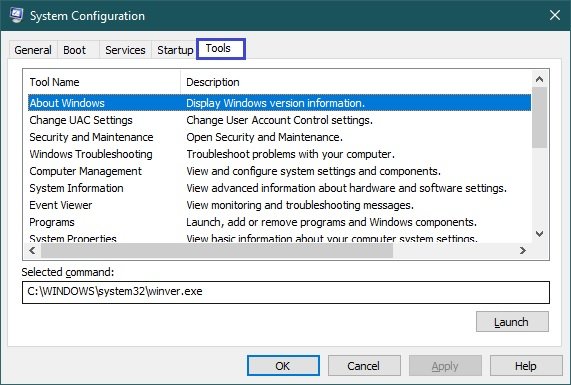
Tools
The Tools tab allows you not only to run the various system configuration tools, but also to see which command is used to run each of them, and if necessary, you can create shortcuts to run the tools you use most often.